
Labs for Tom/Jenny Coordinated Studies Course
Winter 2003
|
|
|
|
Scientific Method Lab |
|
|
Microscope Lab |
Pipette Practice Lab – Interpretation of Gels |
|
Cell Lab |
mt DNA lab CSHL (do early in quarter) |
|
Mitosis & Meiosis |
Hardy-Weinberg – BioRad Alu, Chromosome |
|
Human Genetics – race question??? |
Osteology - Human Bone Lab |
|
Blood Types (human) |
Comparative – mostly Ape (Skull) Anatomy (Primate) |
|
Human Locomotion |
Taxonomy Lab – early hominid/primate |
|
Human Reproduction |
Cladistics – primate |
|
|
Out of Africa vs. Multiregional TESTING |
|
|
Is race biological? |
|
|
|
Exercises/Activities:
Pedigree Analysis
Human Genetics Analysis
Cladograms and other tree structures – primate …
BLAST LAB??
Useful web sites for CS class:
http://medstat.med.utah.edu/kw/osteo/index2.html
http://www.unipv.it/webbio/dfantrop.htm
http://www.oxfordancestors.com/
http://www.nap.edu/readingroom/books/evolution98/contents.html
evolution and the nature of science
http://www.indiana.edu/~ensiweb/less.fs.html
http://archives.math.utk.edu/mathbio/mbSoftware.html
Hardy-Weinberg problems and solutions: http://www.biosci.msu.edu/courses/bs110Lab/hardy/population_genetics.htm http://science.nhmccd.edu/biol/hwe/q1d.html http://kingfish.coastal.edu/biology/bio370/hw.htm
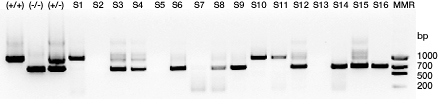
Typical results from Alu polymorphism BioRad Lab


These gels show results obtained in two actual classroom settings. The upper gel shows results generated from Kirk Brown's class at Tracy Joint Union High School. The controls (+/+), (-/-), and (+/-) are seen in the first three lanes, and 15 independent student samples (S1 to S16) are seen in lanes 4—19. The EZ Load DNA mass ruler standard (MMR) is seen in lane 20. The lower gel shows results generated from Skip Lovelady's class at Redwood High School. The controls (+/+), (-/-), and (+/-) are seen in the first three lanes, and 16 independent students samples (S1 to S17) are seen in lanes 4—20.
JLM WILL EDIT THIS LIST FOR CS CLASS!!
i. Bones of the Axial Skeleton {80 bones} A. Skull [28 bones] 1. Cranium: Cranial Bones (8 bones): a. cavities: nasal cavity, oral cavity, orbit b. sutures: sagittal, coronal, lambdoidal, squamosal c. infant skull, fontanels: anterior (frontal) fontanel, posterior (occipital) fontanel, mastoid (posteriolateral) fontanel, sphenoid (anteriolateral) fontanel Frontal bone (1) frontal sinus, supraorbital foramen Parietal bones (2) Occipital bone (1) foramen magnum, occipital condyle Temporal bones (2) mastoid process, styloid process, zygomatic process, carotid canal, external auditory (acoustic) meatus, jugular foramen, mandibular fossa Auditory ossicles (6): Malleus (2) Incus (2) Stapes (2) Sphenoid bone (1) optic canal, superior orbital fissure, sella turcica (hypophyseal fossa of sphenoid bone) Ethmoid bone (1) cribriform plate, crista galli 2. Face: Facial bones (14 bones): a. important structures: zygomatic arch, nasal septum, hard palate b. teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, molars Palatine bones (2) Zygomatic bones (2) temporal process, zygomatic arch Lacrimal bones (2) Nasal bones (2) Vomer bone (1) Maxilla (2) palatine process Inferior Nasal Conchae (2) Mandible (1) mental foramen, mandibular condyle b. Hyoid bone [1] Bone List C. Vertebral Column [26 bones] 4 curvatures: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral Vertebrae: spinous process, superior & inferior articular processes, intervertebral discs, transverse process, costal facets, vertebral body (centrum), vertebral foramen, intervertebral foramen. Intervetebral disks Cervical Vertebrae (7 bones) Atlas (1st vertebra), transverse ligament, transverse foramen Axis (2nd vertebra), dens Vertebra prominens (7th vertebra) Thoracic Vertebrae (12 bones) Lumbar Vertebrae (5 bones) Sacrum (1 fused bone) body of sacral vertebra, sacral foramen, sacral canal, median sacral crest, sacral hiatus, sacroiliac joint Coccyx (1 fused bone) D. Thoracic Cage [25 bones] Costal cartilage Ribs (24 bones or 12 pairs) head (capitulum), neck, tubercle (tuberculum), shaft (body) true ribs: vertebrosternal ribs: 1-7 false ribs: vertebrocostal ribs: 8-10 floating ribs: 11-12 Sternum (1 bone) manubrium, body (gladiolus), xiphoid process, clavicular notch (articulation), jugular notch i. Bones of the Appendicular Skeleton {126 bones} A. Upper Limbs [60 bones] Humerus (2) head, neck, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, intertuberclar sulcus, deltoid tuberosity, medial and lateral epicondyles, capitulum, trochlea, coronoid fossa, olecranon fossa Radius (2) head, neck, radial tuberosity, styloid process Ulna (2) head, olecranon process, coronoid process, styloid process of ulna, radial notch, trochlear (semilunar) notch Carpals (16) Triquetral (Triangular or Triquetrum) (2) Pisiform (2) Hamate (Unciform) (2) Capitate (2) Lunate (Semilunar) (2) Scaphoid (Navicular) (2) Trapezium (Greater multangular) (2) Trapezoid (Lesser multangular) (2) Metacarpals (10) - numbered 1-5 from thumb: head, shaft, base Phalanges (singular: phalanx) (28) distal, middle, and proximal, pollex: head, shaft, base Bone List B. Pectoral Girdle [4 bones] Clavicle (2) sternal end, acromial end, body Scapula (2) glenoid fossa, coracoid process, acromion process, spine, supraspinous fossa, infraspinous fossa, subscapular fossa, vertebral (medial) border, axillary (lateral) border C. Lower Limbs [60 bones] Femur (2) head, neck, greater trochanter, lesser trochanter, linea aspera, medial & lateral epicondyle, medial & lateral condyle, patellar surface Patella (2) Tibia (2) medial & lateral condyle, tibial tuberosity, medial malleolus Fibula (2) head, lateral malleolus Tarsals (14) Talus (2) Navicular (2) Cuboid (2) Cuniforms: Medial, Intermediate, Lateral (6) Calcaneus (2) Metatarsals (10) - numbered 1-5 from medial to lateral: head, shaft, base Phalanges (singular: phalanx) (28) distal, middle, and proximal, hallux: head, shaft, base D. Pelvic Girdle [2 bones] Coxal bone (pelvic bones or os coxa or innominate bones) (2) obturator foramen, acetabulum, sacroiliac joint Ilium: iliac crest, anterior (superior & inferior) iliac spine, iliac fossa posterior (superior & inferior) iliac spine, greater sciatic notch Ischium: ischial tuberosity, lesser sciatic notch Pubis: symphysis pubis (interpubic joint), pubic crest
TOM WILL ADD DIFFERENT COLUMNS FOR CHIMP, GORILLA, …
|
Table 1. |
||
|
Characteristics |
Apes |
Humans |
|
Posture |
Bent
over or quadrupedal "knuckle-walking" common |
Upright or bipedal |
|
Leg and arm length |
Arms longer than legs; arms adapted for swinging, usually among trees |
Legs usually longer than arms; legs adapted for striding |
|
Feet |
Low arches; opposable big toes, capable of grasping |
High arches; big toes in line with other toes; adapted for walking |
|
Teeth
|
Prominent teeth; large gaps between canines and nearby teeth |
Reduced teeth; gaps reduced or absent |
|
Skull
|
Bent forward from spinal column; rugged surface; prominent brow ridges |
Held upright on spinal column; smooth surface |
|
Face |
Sloping; jaws jut out; wide nasal opening |
Vertical profile; distinct chin; narrow nasal opening |
|
Brain size |
80 to 705 cm3 (living species) |
2400 to 2000 cm3 (fossil to present) |
|
Age at puberty |
Usually 10 to 13 years |
Usually 13 years or older |
|
Breeding season |
Estrus at various times |
Continual |
Cladograms from www:
http://img.sparknotes.com/biology/evolution/evidence/gifs/cladogram.gif
http://www.accessexcellence.org/AE/AEPC/WWC/1995/clado-cladogram.gif
http://www.accessexcellence.org/AE/AEPC/WWC/1995/simulation_tree.html
locomotion, foot morphology & cladogram
http://www.uia.ac.be/crc/foot_morphology.html
similarity matrixes to cladograms
http://www.inf.ethz.ch/personal/cannaroz/courses/compbio/week2/week2/week2.html